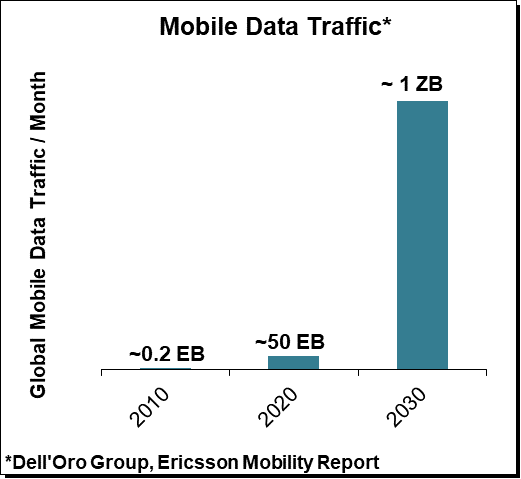
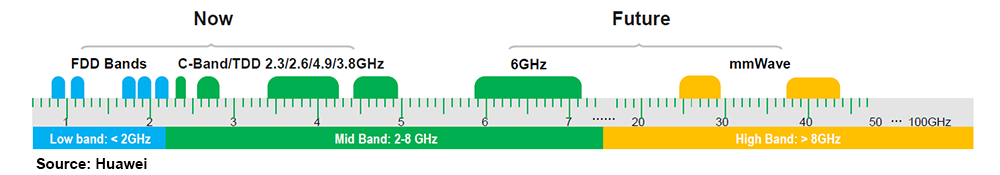
 With 5G now being deployed at full speed in the sub 6 GHz spectrum utilizing both the low-band and the upper mid-band, the focus is shifting to the next spectrum frontier. Even if the upper mid-band in conjunction with Massive MIMO has been a tremendous success story both from an economic and technical perspective providing far more aggregate capacity and throughput upside at a much lower capex than initially envisioned, the baseline scenario suggests mobile data traffic is projected to advance another 15x to 25x over the next decade, surpassing 1 Zettabyte (ZB) per month by 2030. While Massive MIMO and the sub 6 GHz spectrum will go a long way delivering another 5x to potentially 15x of upside, it will likely not be enough to meet the capacity demands of the next decade given the economic constraints the operators are facing.
With 5G now being deployed at full speed in the sub 6 GHz spectrum utilizing both the low-band and the upper mid-band, the focus is shifting to the next spectrum frontier. Even if the upper mid-band in conjunction with Massive MIMO has been a tremendous success story both from an economic and technical perspective providing far more aggregate capacity and throughput upside at a much lower capex than initially envisioned, the baseline scenario suggests mobile data traffic is projected to advance another 15x to 25x over the next decade, surpassing 1 Zettabyte (ZB) per month by 2030. While Massive MIMO and the sub 6 GHz spectrum will go a long way delivering another 5x to potentially 15x of upside, it will likely not be enough to meet the capacity demands of the next decade given the economic constraints the operators are facing.
As a result, all eyes are now on the next 5G spectrum frontier – also known as the 6 GHz spectrum (5.925-7.125 GHz). The Federal Communications Commissions (FCC) recently announced plans that make 1200 MHz of spectrum in the 6 GHz band available for unlicensed use permitting low-power device across the band and standard-power devices in 850 MHz. In order to maximize the overall efficiency and potential impact on the wireless-based economy, it will be imperative for other countries/regions to consider a more balanced approach between the unlicensed and licensed spectrum for the 6 GHz spectrum. The WRC-23 IMT identification for the 6425-7025 MHz band would provide service providers with a solid foundation to realize the 5G vision while at the same time providing consumers, enterprises, and industries with 600 MHz of incremental unlicensed spectrum to manage increasingly congested WiFi networks.
The baseline scenario assumes mobile data traffic will advance 15x to 25x over the next decade. While this initially might appear to reflect a slowdown in relative terms when compared with the growth rates in previous decades, the reality is that we are on track to consume as much data in 2030 as we did in the first twenty years combined of the smartphone era.
And there is no magic. Since the beginning of the first 1G networks through today’s 5G networks, operators have had three basic tools at their disposal to manage capacity growth including introducing more efficient technologies, deploying more cells, and using more spectrum.
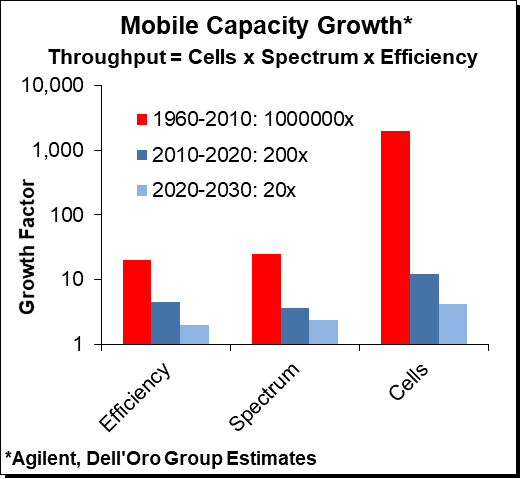
The role of these capacity vehicles has fluctuated over time as the cellular industry has evolved, however, one consistent theme across the board is that the low hanging fruit has been picked, and it is increasingly challenging to extract significant gains.
The shift from 4G to 5G provides ~20% to ~30% of spectral efficiency upside, assuming everything else remains constant. The global macro cell site installed base is advancing at a high single-digit rate annually. Small cell deployments are firming up, but at the same time, co-channel densification without the use of beamforming can increase the interference between the base stations constraining the upside.
Massive MIMO and beamforming technologies address the interference limitations associated with small cell densification by increasing the antenna count at the site, enabling operators to optimize the RF signals directed towards the targeted users while at the same time minimizing interference levels for the remaining users.
So from a technical perspective, Massive MIMO and beamforming represent the next most effective solution of the capacity tool kit. In addition, the more targeted beams are improving the cell range of the base stations, enabling operators to realize equivalent 2 GHz LTE coverage with the upper mid-band, reducing the need to add more sites to compensate for the higher path loss associated with higher operating frequencies producing comparable 5G coverage relative to the 4G coverage.
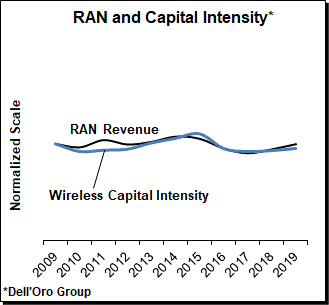
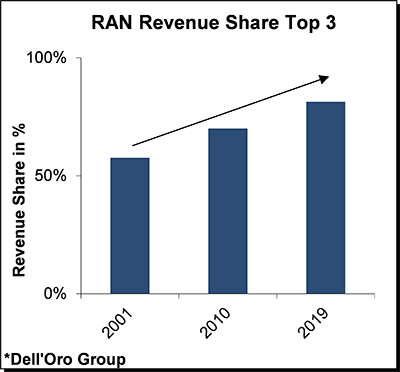
And since the coupling between mobile infrastructure investments and wireless capital intensity remains strong, implying that constrained operator revenue growth will ultimately impact operators’ ability to raise capex, the appeal of Massive MIMO in the mid-band is not difficult to conceptualize. The combination of the capacity upside and the resulting cost per bit benefits by not having to add more sites forms the basis for the success with Massive MIMO – the technology accounted for more than 70% of the 2019 5G mobile infrastructure market.
Not surprisingly, the outlook for Massive MIMO remains favorable, underpinning projections that operators will squeeze as much as they can out of this valuable mid-band spectrum using 32T32R, 64T64R, and eventually 128T128R antennas. It is challenging to pinpoint the exact upside at this juncture but it is not inconceivable that an effective Massive MIMO strategy could produce another 5x to 15x of upside, depending on the spectrum assets.
Regardless, Massive MIMO in the upper mid-band spectrum will not be enough to manage the baseline scenario of total mobile traffic surpassing 1 ZB per month by 2030. And it most certainly will fall short addressing any game-changing device introduction spurring a change in behavior and video consumption utilizing the mobile network. Though video consumption comprised the lion share of the 2019 mobile data traffic, the average smartphone user still spends only around 20 min per day streaming videos on the cellular network, and baseline projections are resting on the assumption that the typical smartphone user will spend no more than 45 minutes per day streaming 4K videos by 2030.
Unlicensed proponents prefer to allocate the majority or all of the 6 GHz band for unlicensed applications, implying they expect mobile data consumption growth will slow at a much faster pace than consensus estimates or Millimeter Wave (mmW) technologies can play an important role addressing the projected shortage.
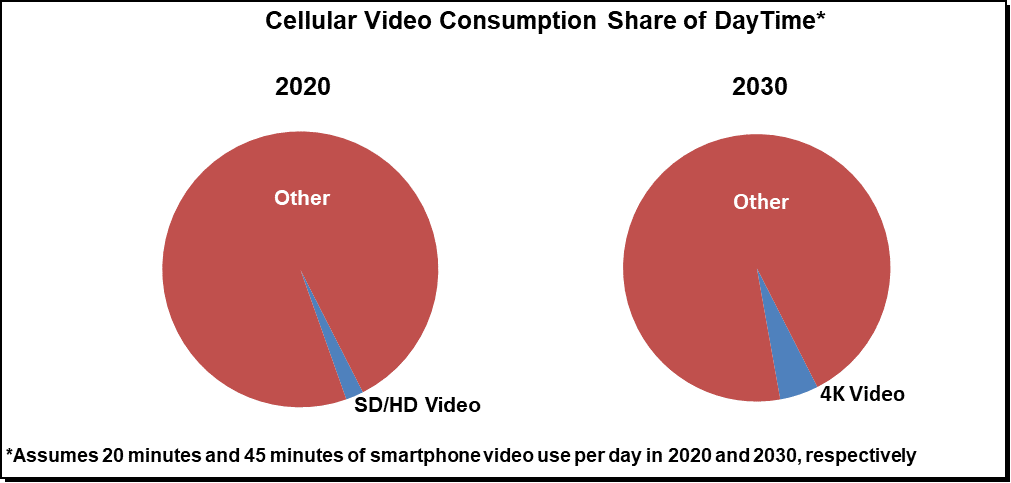
With the 2020 mmW installed base projected to surpass 0.1 M base stations and mmW smartphone devices already delivering Gbps performance, most everyone agrees Millimeter wave (mmW) based 5G NR technologies have advanced at a much faster pace than initially expected. At the same time, it will take time before the economics become compelling enough for early and late majority operators to deploy mmW systems over wider city areas and before the technology can address a significant portion of the overall mobile data traffic given the constrained capex envelopes. Even with upward forecast revisions, mmW based 5G systems are projected to account for less than 5% of the radio shipments over the next five years.
But with 600 MHz of 6 GHz spectrum and macro based EIRP levels, operators would be able to deploy Massive MIMO systems with beamforming utilizing the existing macro grid, thereby providing operators with incremental capacity to navigate not just the baseline growth projections over the next decade within the constrained capex envelope, but also including some margin to navigate new game-changing device introductions or stronger than expected IoT/FWA usage.
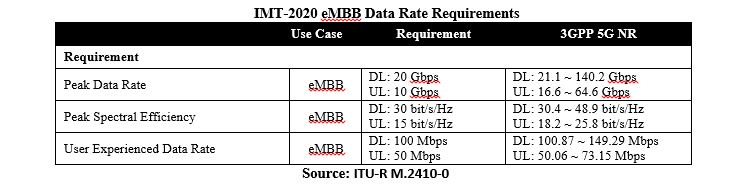
And from a speed perspective, one of the more important requirements in the IMT-2020 standard and vision is that 5G networks should consistently be able to provide 100 Mbit/s data rates to all users – anytime and anywhere. So in addition to dimensioning the networks for capacity, operators also need to design the networks to deliver a consistent experience throughout the cells and the day.
In short, we don’t know exactly how much of the 5G vision will be realized over the next decade. But we do know what tools the operators have at their disposal to navigate this ongoing transition from MBB to eMBB and IoT. And while it is possible that growth on the mobile network will slow at a much faster pace than expected, spectrum policies also need to consider the alternative – what if people end up spending more than 5% of the day streaming video content on the mobile network?
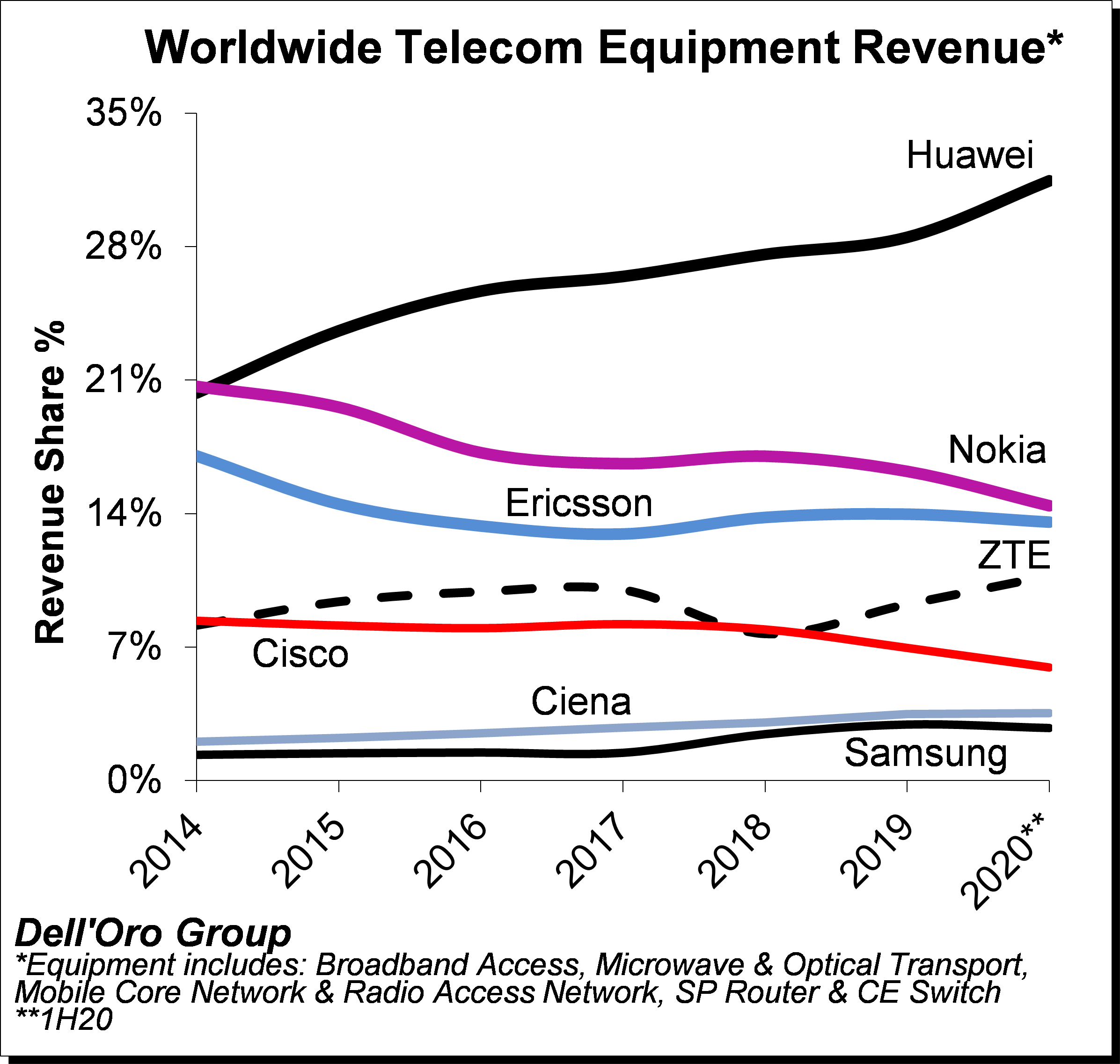 Preliminary readings suggest revenue rankings remained stable between 2019 and 1H20, with Huawei, Nokia, Ericsson, ZTE, Cisco, Ciena, and Samsung ranked as the top seven suppliers. At the same time, revenue shares changed slightly as the Chinese suppliers benefited from large scale 5G rollouts in China.
Preliminary readings suggest revenue rankings remained stable between 2019 and 1H20, with Huawei, Nokia, Ericsson, ZTE, Cisco, Ciena, and Samsung ranked as the top seven suppliers. At the same time, revenue shares changed slightly as the Chinese suppliers benefited from large scale 5G rollouts in China.