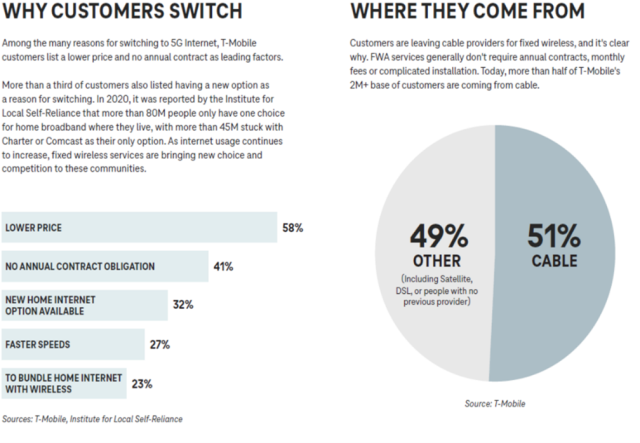
In a blog last year, we detailed how the 5G Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) services provided by T-Mobile, Verizon, and AT&T presented the biggest threat to cable’s dominance of the US fixed broadband market. At the time of that blog (August 2023), T-Mobile had secured 3.2 million FWA subscribers, while Verizon had announced an FWA subscriber base of 2.26 million. At the time, T-Mobile mentioned that around 51% of its subscribers were previously cable customers. While Verizon doesn’t disclose the makeup of its subscriber base, it is safe to assume that they were converting a similar percentage of cable subscribers.
Fast forward to the first quarter of 2024. Not only has the siphoning off of cable broadband subscribers continued, with T-Mobile surpassing 5 million FWA subscribers, but now the operator is expanding its presence in the fixed broadband market by acquiring 50% of Lumos for $950M through a joint venture with EQT. With an additional investment of $500M expected in the 2027/2028 time frame, the Lumos network will be expanded from its current passings total of 320K to 3.5M by the end of 2028.
Why Lumos? Why Now?
T-Mobile has undoubtedly demonstrated not only its potential but also its ability to execute in the area of adding broadband subscribers with an attractively-priced bundle of mobile and fixed services. Much of T-Mobile’s success can be attributed to timing, inflationary pressure on household budgets pushed many cable and DSL subscribers to consider reducing their spending on broadband and other communications services. In fact, in its 2022 “State of Fixed Wireless Access” report, T-Mobile reported that 58% of its FWA subscribers switched specifically because of the lower price. With its FWA subscriber base skewing heavily suburban and rural, T-Mobile also became the only realistic non-cable option for many customers.
But T-Mobile always viewed FWA as opportunistic. Executives clarified recently that “our fixed wireless strategy has always been about selling excess capacity, where we predict normal cell phone usage won’t suck up that 5G capacity.” The company has always known that spectrum limitations and the lure of much higher profit margins per GB of data for mobility customers put a hard ceiling on just how many FWA subscribers the company could expect to support. Additional outlays of mid-band spectrum could potentially resolve any congestion issues in markets with high numbers of FWA subscribers and potential point-to-multipoint mmWave services wouldn’t impact the core 5G sub-6Ghz spectrum.
 Ultimately, though, if T-Mobile wanted to build on its success in Fixed Wireless without running the risk of exhausting its valuable spectrum, it was going to have to either build, buy, or partner with fiber network operators to expand the reach of its broadband service footprint. At first, T-Mobile Fiber announced partnerships with a number of wholesale open access fiber network operators, including Tillman FiberCo, SiFi Networks, and Intrepid Networks. These partnerships would allow T-Mobile to scale its nascent fiber offerings as an ISP without having to own or operate the underlying infrastructure. However, we have heard that T-Mobile has had a difficult time reaching agreements on cost and revenue share with all of these partners, delaying rollouts in strategic markets.
Ultimately, though, if T-Mobile wanted to build on its success in Fixed Wireless without running the risk of exhausting its valuable spectrum, it was going to have to either build, buy, or partner with fiber network operators to expand the reach of its broadband service footprint. At first, T-Mobile Fiber announced partnerships with a number of wholesale open access fiber network operators, including Tillman FiberCo, SiFi Networks, and Intrepid Networks. These partnerships would allow T-Mobile to scale its nascent fiber offerings as an ISP without having to own or operate the underlying infrastructure. However, we have heard that T-Mobile has had a difficult time reaching agreements on cost and revenue share with all of these partners, delaying rollouts in strategic markets.
Back in August, Lumos secured $1.1B in funding from EQT, allowing Lumos to refinance its debt and position itself to expand its fiber footprint across North Carolina, South Carolina, and Virginia. In each of those States, Lumos was securing multiple American Rescue Plan Act (ARPA) Capital Project Fund grants to subsidize the cost of building out fiber networks in a growing number of communities. The company was also well-positioned to secure a meaningful portion of the nearly $3.6B in aggregate BEAD (Broadband Equity, Access, and Development) across those three states.
Partially because of the difficulties in coming to service agreements with its infrastructure partners, but also due to Lumos’ size, geographic focus, exposure to subsidized fiber buildouts, as well as its recent debt refinancing deal with EQT, T-Mobile likely viewed a joint venture with EQT to acquire Lumos as the least risky option to expand its fixed broadband presence in markets where it will continue to compete head-on with both Comcast and Charter, the two operators that have arguably seen the most net broadband subscriber losses to Fixed Wireless.
Under the terms of the deal, Lumos will transition to a wholesale model with T-Mobile as the anchor ISP. This is exactly the type of arrangement T-Mobile has established with some of its other infrastructure partners. However, with its partial ownership of Lumos, T-Mobile can presumably generate better returns and healthier margins from its broadband service offerings. The joint venture also is consistent with T-Mobile’s goal of expanding its market presence and footprint without expending a significant amount of capital. In fact, if you take the $1.4B that T-Mobile will ultimately invest in Lumos as it increases its homes passed from 320K to 3.5M by the end of 2028, T-Mobile’s cost per home passed ends up being somewhat less than $500.
With the Lumos acquisition, T-Mobile Fiber will become available across 11 different States and over 75 unique markets.
It is unlikely that T-Mobile will stop there. The post-pandemic subsidization of fiber networks and providers combined with upcoming BEAD disbursements will result in a significant expansion of fiber across the nation and another increase in the total number of fiber providers, be they wholesale providers, municipalities, electric co-ops, and more traditional ISPs. Not all of these providers will be able to achieve the scale they need to attain a sustainable business in the long term.
Additionally, among the largest operators in the US, it can be argued that some consolidation is necessary since broadband penetration rates are reaching saturation levels and additional growth can only come incrementally.
Therefore, the likelihood of T-Mobile investing in or acquiring select fiber providers, or even acquiring a tier 1 cable operator becomes even greater, particularly if T-Mobile can continue its fixed wireless and fiber subscriber growth.
The push and pull of broadband and wireless subscribers aren’t expected to slow down anytime soon. Certainly, with inflation continuing to put pressure on household budgets, consumers are going to be focused on keeping their communications costs low and looking for value wherever they can find it. That means we are returning to an environment where subscribers take advantage of introductory pricing on services only to switch providers to extend that introductory pricing once the initial offer expires. That shifting and its expected downward pressure on residential ARPU will likely be countered by increasing ARPUs at some providers as they move existing DSL customers to fiber or, in the case of cable operators, move customers to multi-gigabit tiers.
The US broadband market is definitely in for a wild ride over the next few years as the competitive landscape changes across many markets. The net result is certain to be shifts in market share and ebbs and flows in net subscriber additions depending on consumer sentiment. One thing that will remain constant is that value and reliability will remain key components of any subscription decision. The providers that deliver on that consistently will ultimately be the winners.